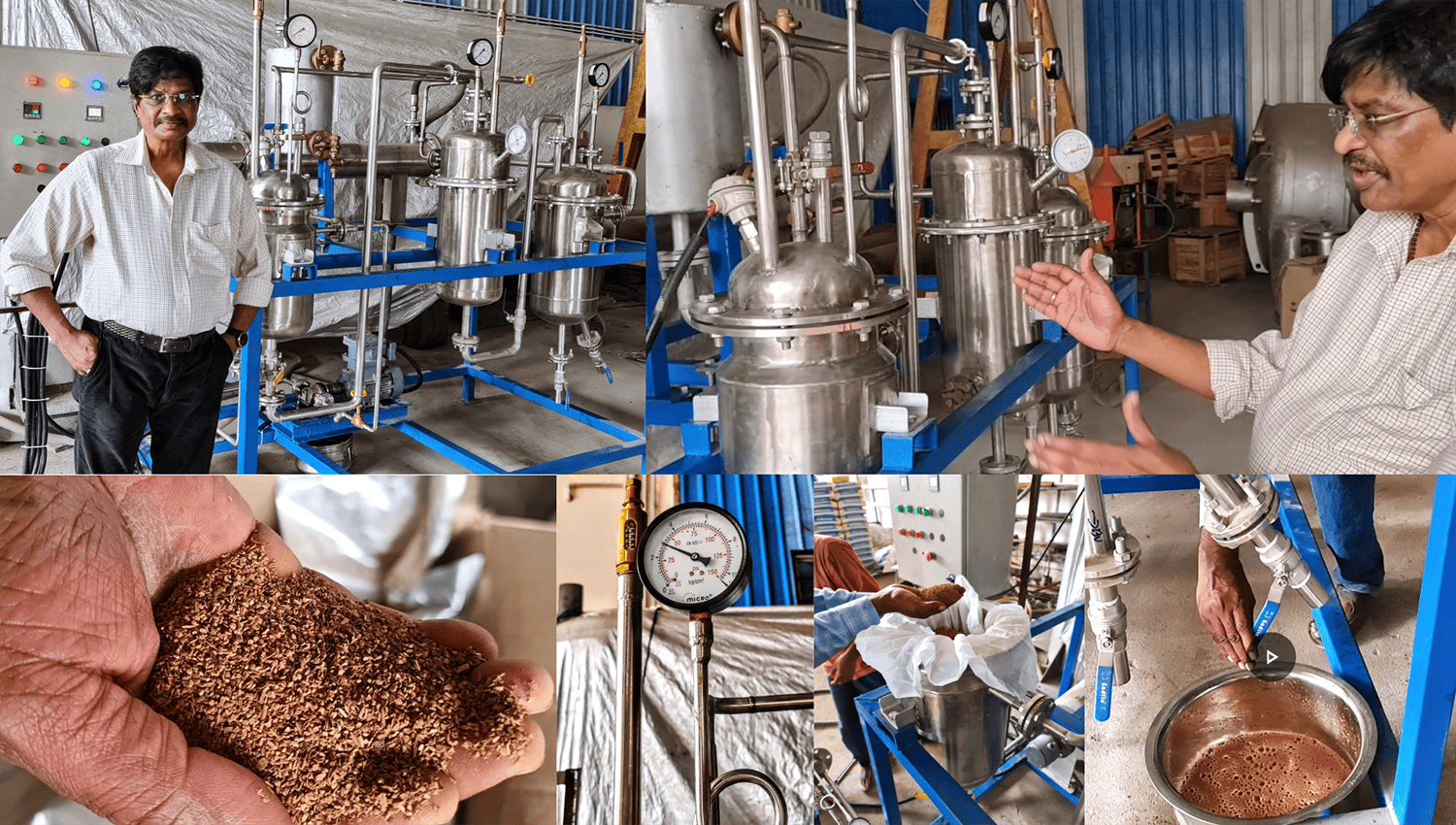

24-September-24
A successful Prototype Equipment for SUBCRITICAL WATER EXTRACTION was tested at the fabricator’s workshop before being dispatched to the customer.
Here is a technical description of the Subcritical Water Extraction (SWE) process applied to extract polyphenols from Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon cinnamon).
Subcritical Water Extraction (SWE) involves using water as the solvent to extract polyphenols from Cinnamomum zeylanicum under controlled temperature and pressure conditions, below the critical point of water (Tc = 374°C, Pc = 221 bar).
Subcritical water extraction uses hot water to solubilize and extract polyphenols from the cinnamon bark. The subcritical conditions allow for efficient extraction while minimizing the degradation of thermally sensitive polyphenols. The process exploits the increased solubility of polyphenols in water at elevated temperatures and pressures.
The yield of polyphenols extracted from Cinnamomum zeylanicum using SWE can vary depending on the process parameters and starting material quality. Typical yields range from 5-15% (w/w) of the dry bark weight.
Here’s a brief comparison of Subcritical Water Extraction (SWE) and Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SCFE) technologies, including their pros and cons based on the properties of the target ingredients:
(Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) is a solvent-free extraction process that utilizes a supercritical fluid, typically carbon dioxide (CO2), as the extraction solvent. The process involves subjecting plant-based ingredients to high pressure and temperature conditions, above the critical point of the fluid, to create a supercritical state.)
Pros:
Cons:
Pros:
Cons:
Note: The exact process parameters and yields may vary depending on the specific SWE equipment and experimental conditions. These are general guidelines, and the optimal extraction technology depends on the specific properties of the target ingredients and the desired outcomes.
© Dr. R. S. Ragavan, C E O.
© 2025 SYNERGY NUTRATEK. All Right Reserved.
Designed & Developed by  Innov Touch Technologies Pvt Ltd.
Innov Touch Technologies Pvt Ltd.